An international collaborative research team led by Prof. Serdar Altin, from Inonu University, Malatya, Türkiye, with co-investigators from the National Centre for Physics (NCP) Islamabad, Pakistan and the Korea Institute of Science and Technology / Korea University of Science and Technology, Seoul, Republic of Korea, has leveraged the power of SESAME’s BM08-XAFS/XRF beamline by probing the intricate role of Ruthenium in enhancing the performance of P2-type Na0.67Mn1-xRuxO2 cathodes via in-operando XAFS of sodium-ion fuel-cells. The element’s site selective in-situ X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy (XAS) data measured at Mn and Ru K-edges elucidated the change in oxidation state and local structure of Mn and Ru sites during charging and discharging cycles. An important result was obtained from time-resolved X-ray Diffraction (TR-XRD) measurement that probed the phase change and lattice parameters during cycling. Their findings, published in the high-impact journal Small (Wiley Online Library), offered valuable insights into the optimization of these cathode materials for next-generation energy storage solutions, such as rechargeable sodium ion batteries. The details of the finding can be found in the published manuscript: https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202406332
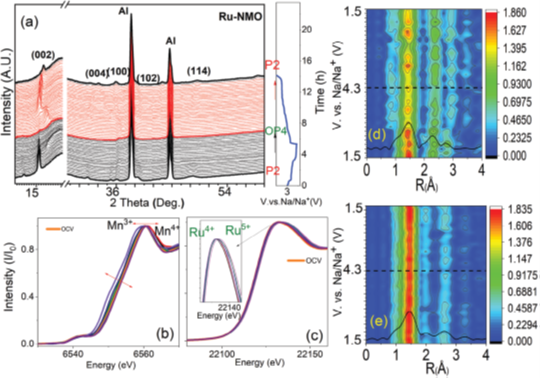
Figure. Structural evaluation of Na0.67Mn0.6Ru0.4O2 cathode via in-operando XRD (a), and in-operando XAFS (b) during charge and discharge processes of the sodium ion battery (left panel), and corresponding Fourier transform (FT) of EXAFS data (right panel).

